In today’s digital age, where uninterrupted connectivity is crucial for businesses and organizations, the concept of a local survivable processor has gained significant traction. This innovative solution offers a robust mechanism to ensure continuous operations even in the face of network disruptions or failures. Let’s delve deeper into the world of local survivable processors, exploring their functionality, benefits, applications, and much more.
Understanding the Importance of Local Survivable Processor
In essence, a local survivable processor serves as a safeguard against network outages by enabling essential computing functionalities to continue operating autonomously at the local level. This capability is particularly critical for businesses reliant on real-time data processing, communication, and decision-making.
How Local Survivable Processor Works
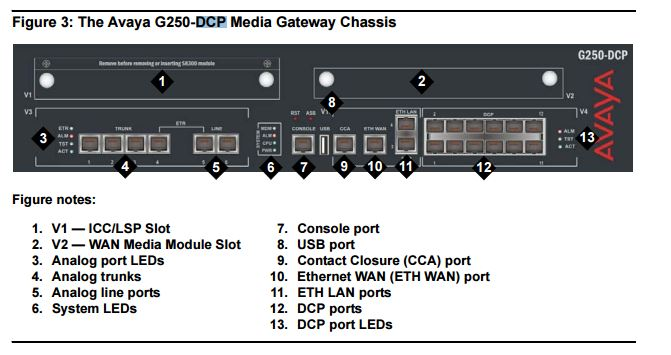
Architecture of a Local Survivable Processor
The architecture of a local survivable processor typically comprises redundant components, including processors, memory units, and communication interfaces. These redundancies ensure that critical functions can seamlessly transition to backup systems in the event of a failure.
Key Components and Functions
Key components of a local survivable processor include fault-tolerant hardware, advanced algorithms for fault detection and recovery, and mechanisms for data synchronization and replication. Together, these elements work cohesively to maintain operational continuity.
Benefits of Using Local Survivable Processor

The adoption of a local survivable processor offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Reliability: By providing a fallback mechanism during network disruptions, local survivable processors enhance the overall reliability of computing systems.
- Improved Resilience: Organizations can withstand network failures more effectively, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
- Cost Savings: While ensuring resilience, local survivable processors help mitigate the financial impact of network outages by averting potential losses associated with downtime.
Applications and Use Cases
Local survivable processors find applications across various industries, including telecommunications, finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. Use cases range from ensuring continuous communication in remote locations to supporting critical financial transactions during network outages.
Comparison with Other Processor Solutions
When compared to traditional processors or cloud-based solutions, local survivable processors offer distinct advantages in terms of reliability, latency, and autonomy. Unlike cloud-based approaches, which rely on external networks, local survivable processors operate independently, minimizing dependencies and potential points of failure.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Local Survivable Processor
When selecting a local survivable processor solution, organizations should consider factors such as scalability, compatibility with existing infrastructure, ease of integration, and vendor support. Conducting thorough evaluations and risk assessments is crucial to ensure that the chosen solution aligns with the organization’s requirements and objectives.
Implementing Local Survivable Processor in Different Industries
The implementation of local survivable processors varies across industries, with each sector leveraging the technology to address specific challenges and requirements. From enabling seamless communication in remote areas to ensuring data integrity in critical infrastructure systems, the versatility of local survivable processors makes them indispensable across various domains.
Future Trends and Developments

As technology continues to evolve, the future of local survivable processors holds promise for further advancements in fault tolerance, scalability, and interoperability. Emerging trends such as edge computing and distributed processing are likely to drive innovation in this space, offering new opportunities for enhancing resilience and performance.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their numerous benefits, local survivable processors face challenges such as complexity in implementation, potential performance trade-offs, and security concerns. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research, innovation, and collaboration among industry stakeholders.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
Several organizations have successfully implemented local survivable processor solutions to overcome network-related challenges and achieve operational resilience. Case studies highlighting these implementations serve as valuable insights for organizations considering adopting similar technologies.
Tips for Maximizing the Efficiency of a Local Survivable Processor
To maximize the efficiency of a local survivable processor, organizations should focus on optimizing system configurations, implementing robust disaster recovery strategies, and conducting regular maintenance and testing. Additionally, staying informed about advancements in hardware and software technologies is essential for leveraging the full potential of local survivable processors.
Security Considerations
Security remains a paramount concern in the deployment of local survivable processors, given their critical role in maintaining operational continuity. Organizations must implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems, to safeguard against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Cost Analysis: Investing in Local Survivable Processor
While local survivable processors offer compelling benefits in terms of resilience and reliability, organizations must carefully evaluate the costs associated with implementation, maintenance, and upgrades. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis can help assess the long-term viability and return on investment of deploying local survivable processor solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, local survivable processors represent a cornerstone of resilient computing, offering a proactive approach to mitigating the impact of network failures and disruptions. By leveraging redundant architectures, advanced algorithms, and autonomous capabilities, these processors empower organizations to maintain operational continuity and adaptability in dynamic environments.


